Have you ever noticed that water and oil always separate when you try to mix them? But the cause of this curious phenomenon isn't just a kitchen riddle. It's caused by an interesting chemistry formula. The concepts of polarity and the hydrophobic effect are learned through the idea behind why oil and water don't mix. In this article, we’ll explain why does oil not dissolve in water and doesn’t mix and explore some real-world examples to illustrate this principle.
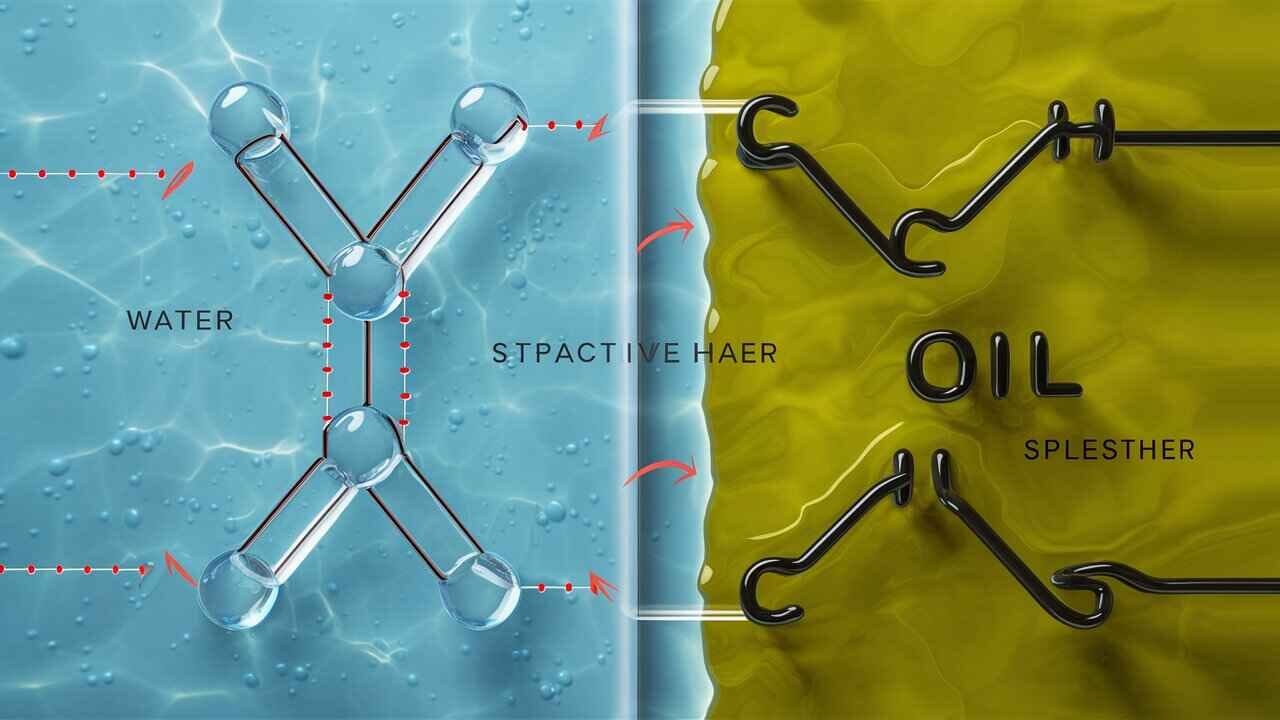
Table of Contents
What Is Dissolution?
Dissolution is the mixing of one substance (the solute) with another (the solvent) such that the solute dissolves into the solvent and these hardy mixing ends. In water, for instance, the water molecules surround and pull apart the sugar molecules to form a homogeneous mixture. However, oil and water do not mix. Let’s explore why.
The Science of Oil and Water
To understand why does oil not dissolve in water, we need to look at the nature of both substances:
Oil: Long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms make up the great majority of oils. Because their molecules are not very different in charge, these structures are said to be nonpolar.
Water: Water is a polar molecule. Around the hydrogen atoms are positive, and around the oxygen atom are negative: we thus have a 'dipole.'
The Role of Polarity
Solubility is a function of polarity in particular. In chemistry, there’s a general rule, like dissolves like. So, polar substances dissolve well in polar things, and nonpolar things dissolve well in things that are nonpolar. Polar water is excellent at dissolving other polar substances (such as soap) but is not good at dissolving nonpolar substances (like oil).
Because oil molecules are nonpolar, they don’t have charged ends to interact with the polar water molecules. Oil and water don't naturally blend; they naturally repel, so they separate clearly.
Is Time Travel Possible In 2050? Science & Religion Explained – Just as the laws of chemistry explain why oil does not dissolve in water, the laws of physics shape our understanding of time. But could time travel be possible by 2050? Explore both scientific and religious viewpoints.
The Hydrophobic Effect
How come oil pulls out of water, and the general separation of nonpolar substances from water? Basically, because of their polar nature, water molecules stick together. Water molecules will then organize themselves when oil is added to water to avoid contact with the oil. The resulting energy results in a phenomenon that minimizes what energy is required of the system, such that the oil and the water separate into different layers.
Real-World Examples of Oil and Water Separation
This effect can be seen in various everyday scenarios:
Cooking: Whisk or shake oil and vinegar dressings if you don’t use them right away.
Environmental Science: When oil spills into oceans or lakes, they form a noticeable sheen above the water that makes it difficult for dams to remove.
Biology: The cell membrane has a layer of fat (lipid) in it that repels water; this helps keep the cell together while protecting it from what’s on the outside.
Why does oil not dissolve in water, the main reason?
Whether two substances mix depends on their polarity. Water is polar, meaning it has positive and negative ends that help its molecules stick together. Oil, however, is nonpolar, meaning its molecules have no charge difference.
A simple rule in chemistry is like dissolves like: polar substances mix with polar solvents, and nonpolar substances mix with nonpolar solvents. Since water and oil have different polarities, they do not attract each other. Instead, oil molecules clump together, while water molecules bond with their kind.
This is the main reason why oil does not dissolve in water; they are simply too different to mix!
How Does Recycling Help Save Energy? – Understanding molecular behavior, like why oil and water don’t mix, helps us see how science shapes our world. Similarly, recycling plays a key role in conserving resources and energy. Discover how it helps.
Can We Make Oil and Water Mix?
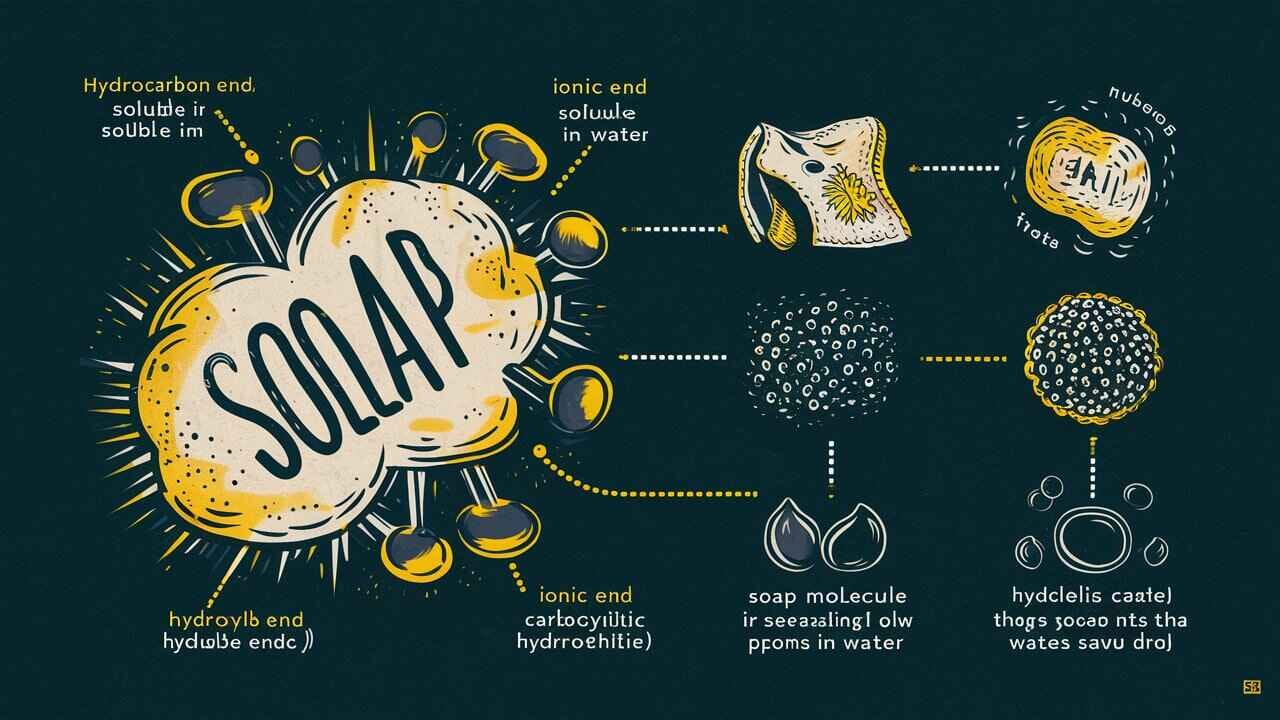
Oil and water don’t mix on their own, but they can be made to mix for a short time. This happens when we add an emulsifier, like soap. Soap molecules have two special ends, one that loves water (hydrophilic) and one that avoids water (hydrophobic). When soap is added, it surrounds the oil droplets, breaking them into tiny pieces that can stay in the water for a while. This is how soap helps clean greasy dishes and how products like lotion and milk stay mixed. This simple process explains why does oil not dissolve in water and how science makes them work together!
Disadvantages Of Renewable Energy – Oil and water don’t mix due to their molecular properties, just as renewable energy, despite its benefits, comes with its challenges. Learn about the disadvantages of renewable energy.
Have you ever noticed that oil and water don’t mix? Why does oil not dissolve in water? The answer is simple: oil and water are made of different types of molecules.
Water molecules are polar, meaning they have a slight electrical charge. Oil molecules are nonpolar, so they don’t have a charge. Since opposites attract, water molecules stick together and push oil away. This is why oil floats on water instead of mixing.
However, scientists have found a way to make them mix using emulsifiers. These special substances help oil and water mix, making products like mayonnaise, lotion, and milk.
So, why does oil not dissolve in water? It all comes down to how molecules behave. This simple idea helps us understand chemistry and how things work in nature and technology!
For a deeper understanding of why oil does not dissolve in water, check out this detailed explanation from Florida State College.
